
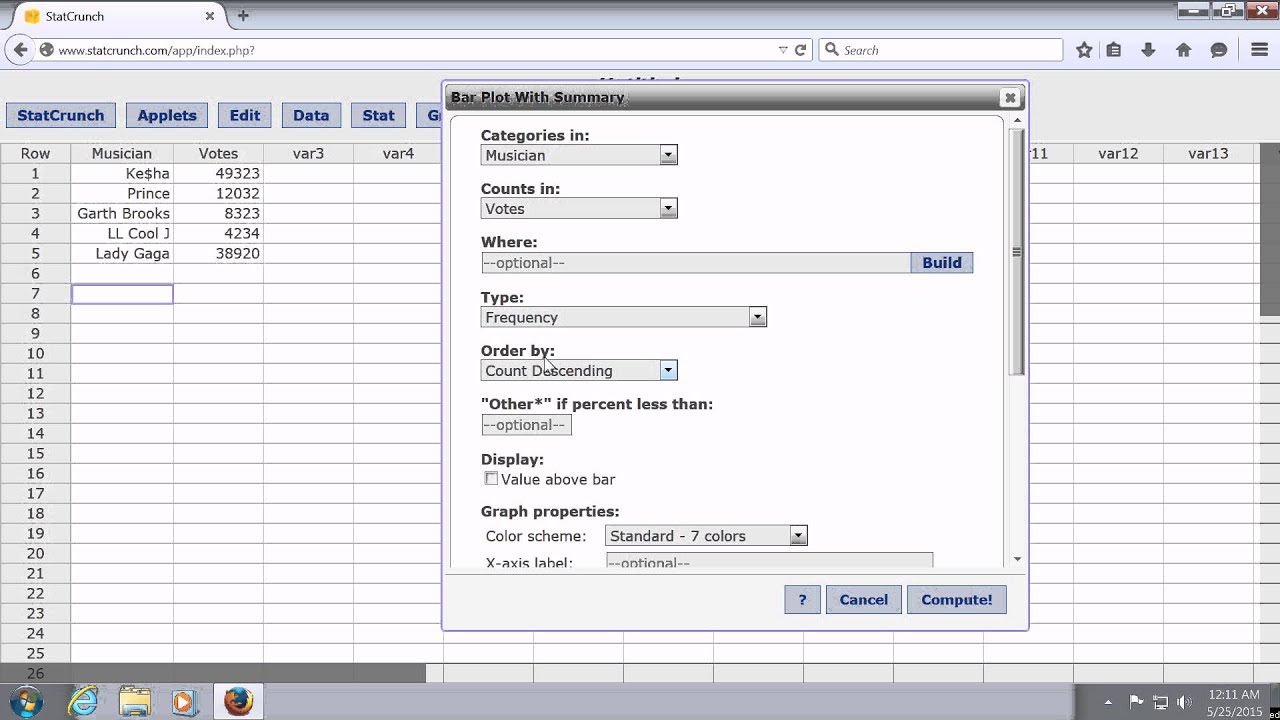
Thankfully, ranking data is not a difficult task and is easily achieved by working through your data in a table. In some cases your data might already be ranked, but often you will find that you need to rank the data yourself (or use SPSS Statistics to do it for you). You will not always be able to visually check whether you have a monotonic relationship, so in this case, you might run a Spearman's correlation anyway. On the other hand if, for example, the relationship appears linear (assessed via scatterplot) you would run a Pearson's correlation because this will measure the strength and direction of any linear relationship. That is, if a scatterplot shows that the relationship between your two variables looks monotonic you would run a Spearman's correlation because this will then measure the strength and direction of this monotonic relationship. However, you would normally pick a measure of association, such as Spearman's correlation, that fits the pattern of the observed data. That is, you can run a Spearman's correlation on a non-monotonic relationship to determine if there is a monotonic component to the association. For example, the middle image above shows a relationship that is monotonic, but not linear.Ī monotonic relationship is not strictly an assumption of Spearman's correlation. Monotonicity is "less restrictive" than that of a linear relationship. Spearman's correlation measures the strength and direction of monotonic association between two variables.
Why is a monotonic relationship important to Spearman's correlation? Examples of monotonic and non-monotonic relationships are presented in the diagram below: What is a monotonic relationship?Ī monotonic relationship is a relationship that does one of the following: (1) as the value of one variable increases, so does the value of the other variable or (2) as the value of one variable increases, the other variable value decreases. However, Spearman's correlation determines the strength and direction of the monotonic relationship between your two variables rather than the strength and direction of the linear relationship between your two variables, which is what Pearson's correlation determines. Although you would normally hope to use a Pearson product-moment correlation on interval or ratio data, the Spearman correlation can be used when the assumptions of the Pearson correlation are markedly violated. You need two variables that are either ordinal, interval or ratio (see our Types of Variable guide if you need clarification).
Spearman's correlation coefficient, (ρ, also signified by r s) measures the strength and direction of association between two ranked variables. The Spearman's rank-order correlation is the nonparametric version of the Pearson product-moment correlation. When should you use the Spearman's rank-order correlation?

#STAT CRUNCH HOW TO#
If you want to know how to run a Spearman correlation in SPSS Statistics, go to our Spearman's correlation in SPSS Statistics guide.
This guide will tell you when you should use Spearman's rank-order correlation to analyse your data, what assumptions you have to satisfy, how to calculate it, and how to report it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
